Friday, January 23, 2015
CCNA Access List Control (ACL) Simulation
5:16 AM
No comments
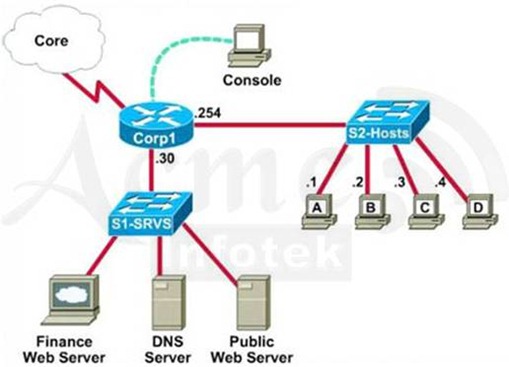
A
network associate is adding security to the configuration of the Corp1
router. The user on host C should be able to use a web browser to access
financial information from the Finance Web Server. No other hosts from
the LAN nor the Core should be able to use a web browser to access this
server. Since there are multiple resources for the corporation at this
location including other resources on the Finance Web Server, all other
traffic should be allowed.
Sunday, January 18, 2015
Installation Ubuntu
4:36 AM
No comments
In this chapter we will install Ubuntu. If you would like to follow along, get your copy of Ubuntu from the following link:
Make
sure that the first boot device in BIOS is set to your CD/ROM (if you
are installing Ubuntu from a CD/ROM) or USB device (if you are
installing Ubuntu from an USB device). You can learn how to do that in
the previous chapter. After you set up the boot order, save the changes
and restart your computer.
Make sure that you
have enough space on your computer to install Ubuntu. It is also
recommended that your computer is connected to the Internet.
The
first thing we need to specify after starting the installation is the
language and whether we would like to install Ubuntu or just try it:
Types of Ethernet cabling
3:50 AM
No comments
There
are three cable types commonly used for Ethernet cabling: coaxial,
twisted pair, and fiber-optic cabling. In today's LANs, the twisted pair
cabling is the most popular type of cabling, but the fiber-optic
cabling usage is increasing, especially in high performance networks.
Coaxial cabling is generally used for cable Internet access. We will
explain all three types of cabling. We will also explain a difference
between a straight-through and crossover cable.
Coaxial cabling
Coaxial
cable has an inner conductor that runs down the middle of the cable.
The conductor is surrounded by a layer of insulation which is then
surrounded by another conducting shield, which makes this type of
cabling resistant to the outside interference. This type of cabling
comes in two types, thinnet and thicknet. Both types have a maximum
transmission speed of 10 Mbps. Coaxial cabling was used for computer
networks, but today are largely replaced by twisted-pair cabling (Photo
credit: Wikipedia)
How to configure open shortest path first routing protocol
3:13 AM
No comments
In this article I will demonstrate an example of OSPF Routing
configuration. We will use four different series router so you can get
familiar with all different platform covered in CCNA exam. Create a
topology as shown in figure.
VLAN
12:11 AM
No comments
VLAN or Virtual Local Area Network is a phenomenon which is used to
logically separate or combine a network. It is used to configured one or
more devices, so that they can communicate, as if they were attached to
the same wire, when in fact they are located on a number of different
LAN segments. Because VLANs are based on logical instead of physical
connections, they are extremely flexible.
Networking Cables and Connections
12:02 AM
No comments
In
order for the communication to take place, cables play important role.
Cable is the medium through which information usually moves from one
network device to another. There are several types of cable which are
commonly used with LANs. The type of cable chosen for a network is
related to the network's topology, protocol, and size.
There are various types of cables used in networks as follows.
There are various types of cables used in networks as follows.
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Fiber Optic Cable